Hygiene regulations in the foodservice industry: what you need to know.
At the start, hygiene regulations in the foodservice industry often seem like a tiresome obligation involving a lot of red tape. But once the HACCP concept is in place and the control measures have become routine, the topic can be seen in a new light: hygiene becomes a seal of quality that distinguishes your business and makes it a safe place for its guests. But what are the current hygiene regulations? What do you need to be aware of as a foodservice business? And how do you implement these regulations in your business? You will find the answers on this page.
1 Why is hygiene so important in the foodservice industry?
Hygiene affects all areas of life and aims to prevent infections, stop the spread of diseases and maintain health. Coronavirus has demonstrated the dangers posed by pathogens and how important protective hygiene measures are. This is especially true for the foodservice industry – wherever food is handled, strict compliance with hygiene standards is essential. This is because food is an ideal breeding ground for microorganisms and can be infected by pathogens on its way from harvest, slaughter or production and reach foodservice tables. It only takes one link in the hygiene chain to be weakened and food can be contaminated with residues and pollutants that are hazardous to health. To protect our health, strict hygiene regulations therefore exist to govern the production, storage, processing and preparation of food.
Cross contamination – the invisible danger
The problem
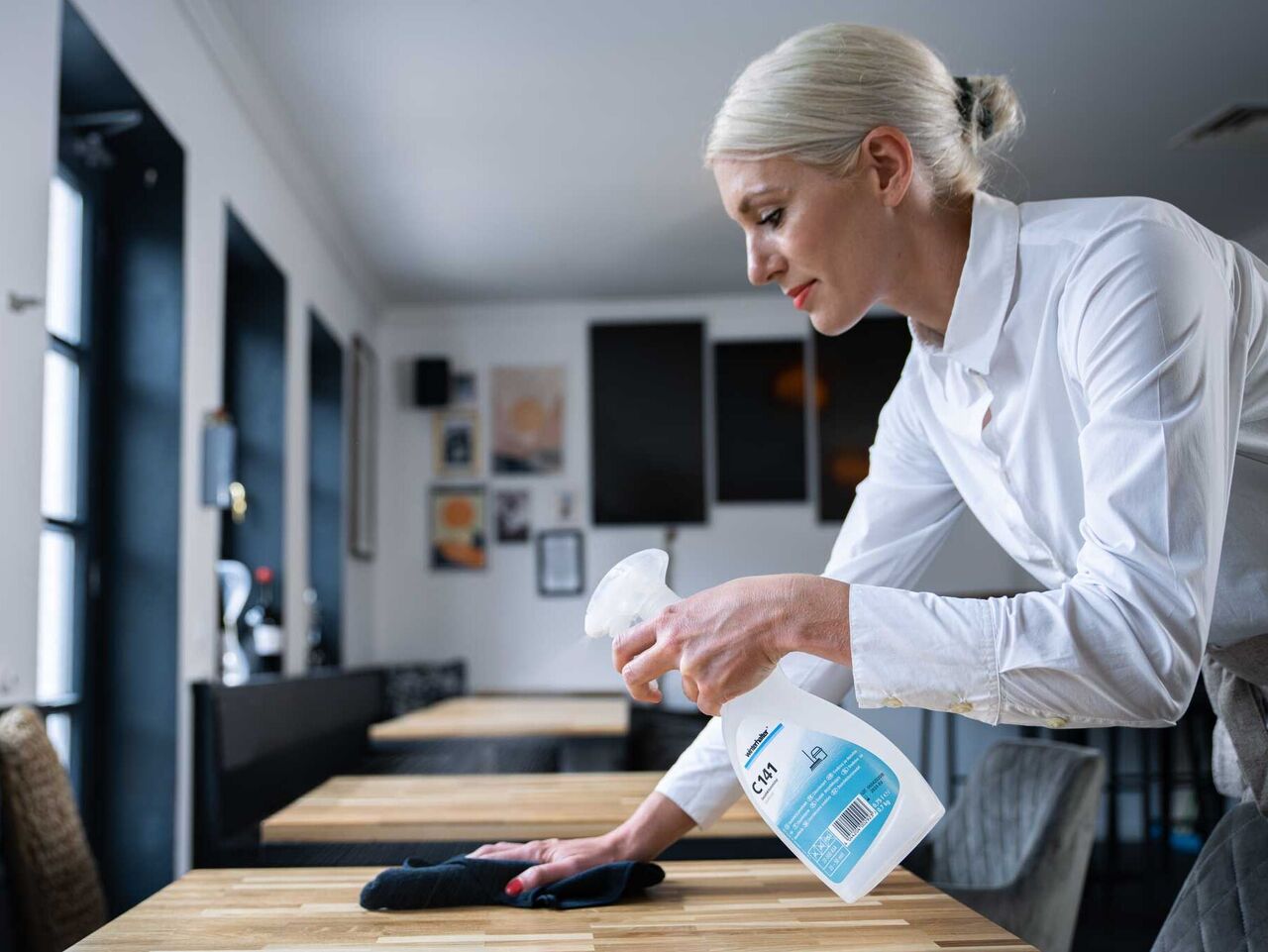
Foodservice kitchens carriy a special risk because they involve both clean and unclean areas. On the one hand, there is the area for clean work, such as the preparation, cooking, portioning and serving of food. This includes the provision of clean dishes. On the other hand, there is the area for unclean work, such as washing lettuce and vegetables, preparing raw animal parts or washing dishes and disposing of waste. This is where cross-contamination can occur, when pathogenic germs unintentionally find their way from unclean areas back into the clean processing area of the kitchen.
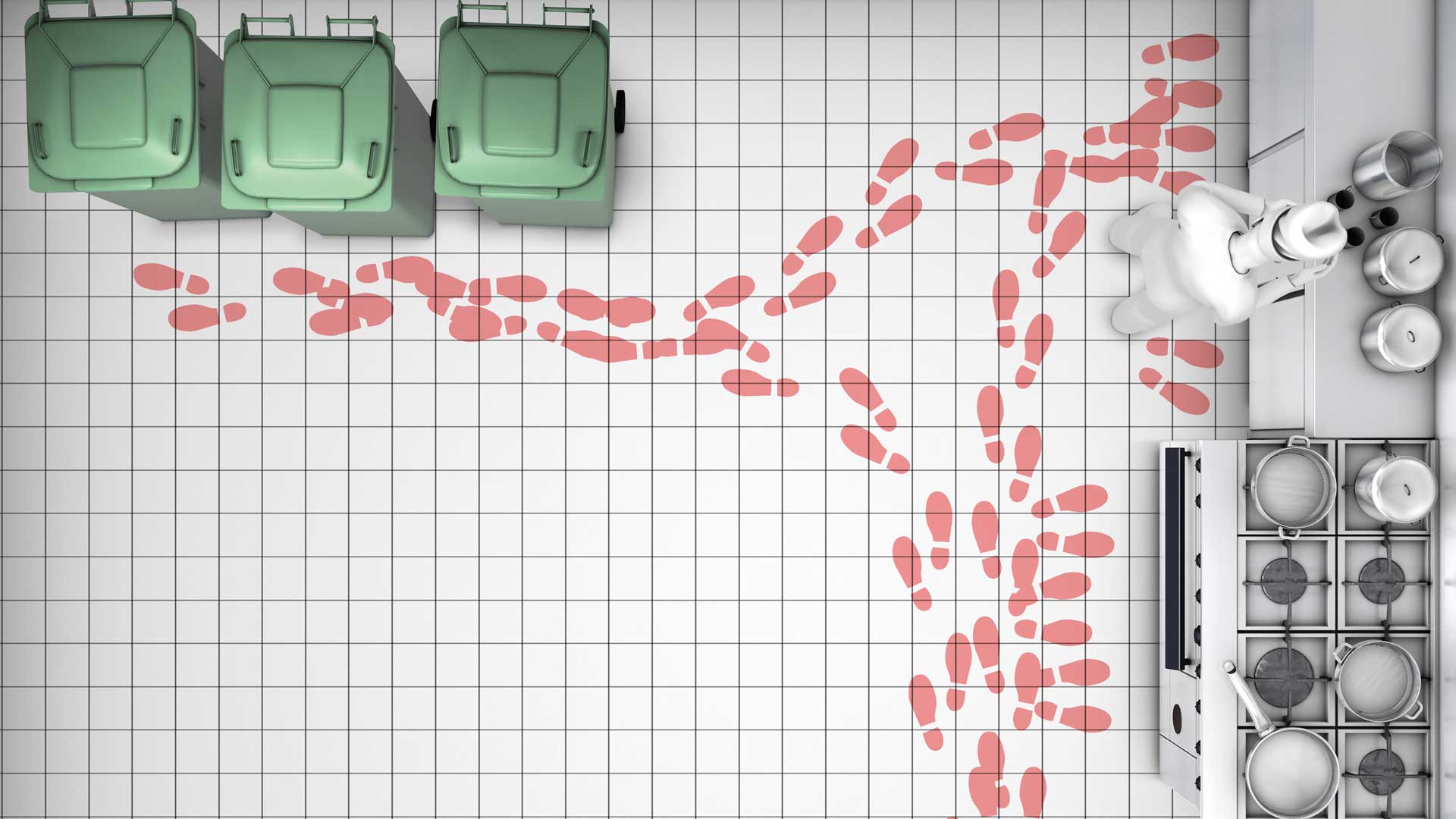
The solution
Cross-contamination can be prevented if clean and unclean areas are consistently separated. This starts in the kitchen planning phase and must be observed each and every day – by every employee. In the individual processing areas of the kitchen for example:
- Moving rubbish bins out of the kitchen or ideally using an organic waste disposal system
- Using different chopping boards and cleaning or disinfecting them thoroughly after use.
- Processing food that is susceptible to germs in a separate area (e.g. poultry, meat, eggs). Washing your hands thoroughly and cleaning and disinfecting all utensils and work surfaces that have been used.
- Using non-woven cleaning cloths, washing them out regularly and disinfecting or disposing of them at the end of the day.
- Using separate sinks and hand basins

2 Your obligations as a foodservice business.
For many years now, strict hygiene regulations have applied to the food sector and therefore, the foodservice industry. The different national laws were harmonised by the European Parliament on 1 January 2006 and replaced by the new Food Hygiene Regulation (EC) No. 852/2004 This is supplemented by a number of other regulations: for example, the Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 with specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin.
This is what you need to ensure
Anyone involved in food production or processing must ensure good hygiene practices on their premises. That is why as a foodservice business, you have certain obligations. Here are the most important ones.
3 Foodservice and HACCP
As a foodservice business, you are obliged to set up, regularly implement and, if necessary, adapt an HACCP self-checking system and must provide proof of this to the food inspection authority. Don’t worry: this sounds quite complicated at first and a lot of effort, but it’s more straightforward than it seems. We will show you how to create a secure HACCP concept or HACCP system.
4 Important hygiene measures in the foodservice industry
Depending on the size and type of foodservice establishment, different hygiene measures must be taken based on the HACCP concept. The following six components are standard in the foodservice industry.
5 Food inspection in the foodservice industry
Inspectors from the official food control authority (“Lebensmittelüberwachung”) or veterinary office visit over half of all businesses once a year without prior notice. It is the “inspection of inspections” and check whether you comply with the regulations on hygiene and disinfection and have taken all the necessary measures to be able to serve safe and healthy food to your guests.
Who do they inspect?
The food monitoring authority primarily inspects establishments where there is an increased risk – for example, if perishable food is handled (meat and fish, eggs, dairy products, etc.). Right at the top of the list are businesses that have received complaints. A suspicion or a complaint is checked without delay.

What is inspected?
First and foremost, the premises and the kitchen equipment are inspected, the employees’ work procedures are observed and food samples are taken. Bookkeeping records and documentation of the measures and controls that are part of the HACCP concept are also audited.

What happens in the event of complaints?
If the complaints are minor, the business owner just receives a briefing and a subsequent follow-up inspection. In the event of serious violations, the business owner receives a fine. If there is an acute health risk to guests or staff, the business may be forced to close and criminal proceedings may be initiated.

The inspectors pay particular attention to




















